What is the 30-year Treasury bond?
Contents
- 1 What is the 30-year Treasury bond?
- 2 What is the risk of Treasury bills?
- 3 Are Treasuries bonds?
- 4 Are Treasury bills highly marketable?
- 5 Are T-bills safer than CDs?
30-year treasury bonds are bonds issued by the U.S. government and have a maturity of 30 years. Other securities issued by the US government include treasury bills, notes and inflation-protected securities (TIPS).
Why is a 30-year bond important? The 30-year bond was reintroduced to diversify Treasury funding opportunities and expand the investor base. The reintroduction of the bond also needed to stabilize the average maturity of public debt. … The bond also served as an important benchmark against which other long-term securities were measured.
What is a treasury bond in simple terms?
Treasury bonds (T-bonds) are government debt securities issued by the US federal government with a maturity of more than 20 years. Treasury bonds earn periodic interest until maturity, with the owner also being paid a nominal amount equal to the principal.
What is an example of a Treasury bond?
For example, treasury bills or treasury bills are short-term bonds with a maturity of several days to 52 weeks. Treasury bills or T-bonds are very similar to treasury bonds in that they pay a fixed interest rate every six months to maturity.
What is a Treasury bond and how does it work?
Treasury bills and bonds are securities that pay a fixed interest rate every six months until the maturity of the security, when the treasury pays the nominal value. The only difference between them is their length to maturity. Treasury bills mature in more than one year, but not more than 10 years from the date of issue.
What is the purpose of Treasury bond?
When you buy a treasury bond, you are essentially lending money to the federal government. Because the U.S. government is willing to repay your loan, credit risk or default risk is extremely low. The Treasury Department can always increase taxes or use other methods to repay your debt.
What is the current 30 year Treasury bond rate?
| Value from the previous market day | 2.14% |
|---|---|
| Change from the previous trading day | 4.21% |
| Value from 1 year ago | 1.93% |
| Change from a year ago | 15.54% |
| Frequency | Market Daily |
What is the 10 year Treasury bond paying?
A 10-year treasury bond is a debt obligation issued by the United States government with a maturity of 10 years after initial issuance. A 10-year treasury bill pays interest at a fixed rate once every six months and pays the nominal value to the owner at maturity.
What is the return on a 30 year bond?
Yields on 30-year U.S. bonds are expected to trade at 2.28 percent by the end of this quarter, according to global macroeconomic trading models and analysts’ expectations.
What is the current Treasury I Bond rate?
The combined rate for bonds I issued from November 2021 to April 2022 is 7.12 percent. This rate applies for the first six months of your bond ownership.
Does the US Treasury still issue 30 year bonds?
Treasury bonds pay a fixed interest rate every six months until maturity. They are issued for a period of 20 or 30 years. You can buy TreasuryDirect from us at TreasuryDirect. … (We no longer sell bonds in Legacy Treasury Direct, which we are phasing out.)
Are US savings bonds still available?
As of 1 January 2012, paper savings bonds are no longer sold in financial institutions. This action supports the Treasury’s goal of increasing the number of electronic transactions with citizens and businesses. NOTE: Tax issues? … The only way to buy EE bonds is to buy in electronic form at TreasuryDirect.
When did the Treasury stop issuing 30 year bonds?
The U.S. government is completing the issuance of a 30-year bond – October 31, 2001. The Treasury says the debt bond no longer meets its financing needs.
Does the Treasury issue 30 year bonds?
30-year treasury bonds are bonds issued by the U.S. government and have a maturity of 30 years. … Treasuries with a maturity of 30 years pay interest semi-annually until they mature and pay the nominal value of the bond upon maturity.
What is the risk of Treasury bills?

Thus, the risks of investing in T-bonds are opportunity risks. That is, the investor could have gotten a better return elsewhere, and time will tell. The dangers lie in three areas: inflation, interest rate risk and opportunity costs.
Why are treasury bills risk-free? Debt obligations issued by the U.S. Treasury Department (bonds, bills, and especially treasury bills) are considered risk-free because they are backed by the “full faith and credit” of the U.S. government. Because they are so secure, the return on risk-free assets is very close to the current interest rate.
Can you lose money in treasury bills?
Can you lose money by investing in bonds? Yes, you can lose money when selling a bond before the maturity date because the sale price could be lower than the purchase price.
Is it safe to invest in treasury bills?
Treasury bills are one of the safest investments, but their returns are low compared to most other investments. Opportunity cost and risk need to be considered when deciding whether treasury bills are eligible for the retirement portfolio. In general, treasury bills may be appropriate for investors who are close to or retired.
Are Treasury bills less risky?
The most commonly used risk-free rate is either a current treasury bill or a treasury bill, a rate or yield on long-term government bonds. Treasury bills are considered almost risk-free because they are fully supported by the US government.
Why are Treasury bills considered risk-free?
Why invest in treasury bills? You get interest in advance. … Investing in treasury bills is virtually risk-free as there is little chance that the Philippine government will not pay its debt in local currency.
Do Treasuries have interest risk?
Treasuries are indeed free of credit risk, but they are subject to interest rate risk. … If an investor holds a treasury security until its maturity, this is not a factor.
Do treasury bills have interest risk?
The Treasury bill does not pay coupons – “interest payments” – which leads to maturities. Treasury bills can inhibit cash flow for investors who need a steady income. Treasury bills have interest rate risk, so their rate could become less attractive in an environment of rising rates.
Do Treasury bonds have interest rate risk?
Interest rate risk is common to all bonds, even American ones. treasury bonds. The maturity and coupon rate of a bond generally affect how much its price will change as a result of changes in market interest rates.
Is it safe to invest in treasury bills?
Treasury bills are one of the safest investments, but their returns are low compared to most other investments. Opportunity cost and risk need to be considered when deciding whether treasury bills are eligible for the retirement portfolio. In general, treasury bills may be appropriate for investors who are close to or retired.
Why do people still invest in treasury bills?
The primary advantage of U.S. Treasury securities is security. No other investment carries such a strong guarantee that interest and principal will be paid on time. Because these payments are predictable, many people invest in them to preserve and increase their capital and earn a reliable income.
Are Treasury bonds a safe investment?
Treasury securities are issued by the federal government and are considered among the safest investments you can make, as all treasury securities are backed by the “full faith and credit” of the U.S. government.
Are Treasury bills a safe investment?
Treasury bills are considered safe and conservative investments as they are supported by the US government. Treasury bills are usually held until the maturity date. However, some owners may want to pay out the money before maturity and make short-term interest income by reselling the investment in the secondary market.
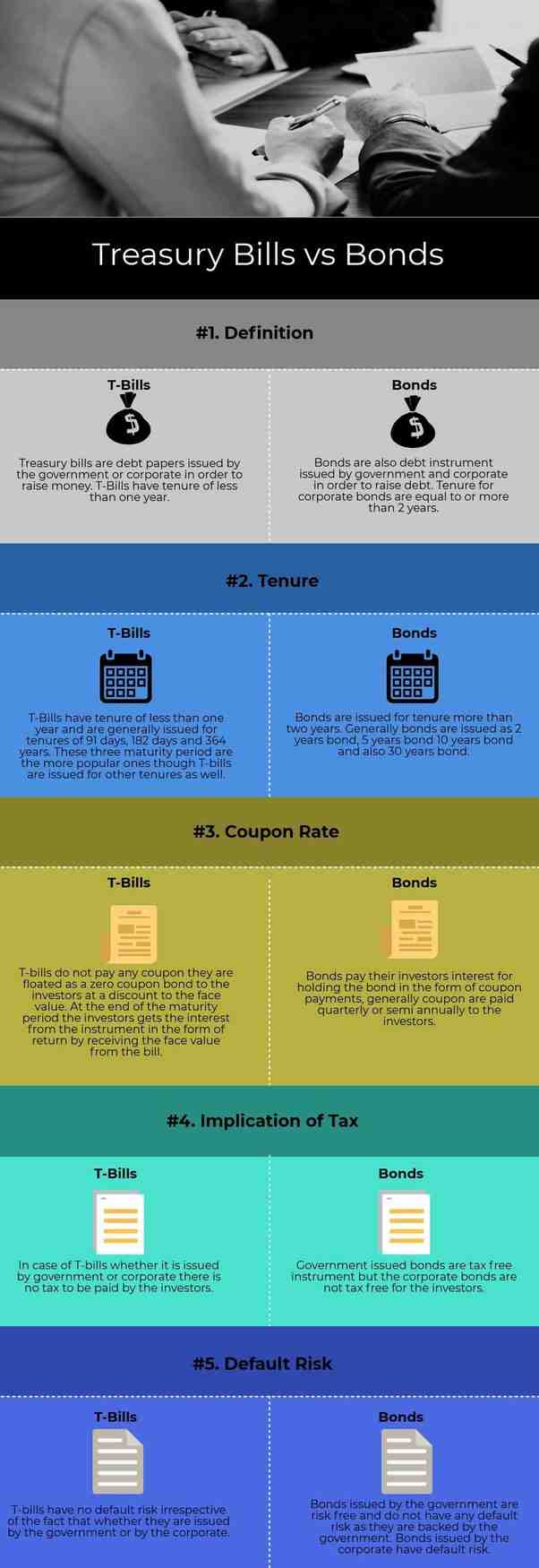
Are Treasuries bonds?
Treasury bonds (T-bonds) are U.S. fixed-rate debt securities with a maturity of between 10 and 30 years. … Together with treasury bills, treasury bills and inflation-protected treasury securities (TIPS), treasury bonds are one of four virtually risk-free government securities.
Are bonds and vaults the same thing? Treasury bills are short-term debt securities issued by the federal government that mature within one year of purchase. Bonds, on the other hand, come in a number of variants and usually come with much longer maturities.
What are considered Treasuries?
Treasury securities are issued by the federal government and are considered among the safest investments you can make, as all treasury securities are backed by the “full faith and credit” of the U.S. government.
What are the 4 main types of treasury bonds?
Treasury bonds (T-bonds) are one of four types of debt issued by the U.S. Treasury Department to finance U.S. government spending activities. The four types of debt are treasury bills, treasury bills, treasury bonds and inflation-protected treasury securities (TIPS).
What are Treasury bonds examples?
For example, treasury bills or treasury bills are short-term bonds with a maturity of several days to 52 weeks. Treasury bills or T-bonds are very similar to treasury bonds in that they pay a fixed interest rate every six months to maturity.
What are examples of Treasuries?
Treasury securities and programs
- Treasury bills. Treasury bills are short-term government securities with a maturity of several days to 52 weeks. …
- Treasury bills. …
- Treasury bonds. …
- Inflation-protected securities (TIPS) …
- Savings bonds series I. …
- EE series savings bonds.
Is a Treasury bill a bond?
Treasury bills are zero-coupon bonds that are usually sold at a discount, and the difference between the purchase price and the face value is your interest charged.
What is the difference between a Treasury bill and a bond?
The main difference between the two is the maturity. While treasury bills have a maturity of up to 1 year, government bonds are investment instruments with a maturity of more than one year. If you wait until maturity, you will repay your principal along with interest.
What is a Treasury bill classified as?
Treasury bills or treasury bills have a maximum maturity of 364 days. Thus, they are categorized as money market instruments (the money market operates with assets with a maturity of less than one year).
What are the 3 types of Treasury bonds?
| Type of treasury | Minimum denomination | Maturity |
|---|---|---|
| Treasury bonds | $ 100 | 20 and 30 years |
| Inflation-hedged securities (TIPS) | $ 100 | 5, 10 and 30 years |
| Variable rate notes (FRN) | $ 100 | 2 years |
| Separate trading in registered interest and equity (STRIPS) | $ 100 | It varies |
What are the 4 main types of Treasury bonds?
Treasury bonds (T-bonds) are one of four types of debt issued by the U.S. Treasury Department to finance U.S. government spending activities. The four types of debt are treasury bills, treasury bills, treasury bonds and inflation-protected treasury securities (TIPS).
What are the three types of Treasury securities?
The federal government offers consumers and investors three categories of fixed-income securities to fund its operations: treasury bonds, treasury bills, and treasury bills. 1ï »¿Each security has a different maturity and each pays interest in a different way.
What are the 3 common bonds?
There are three main types of bonds:
- Corporate bonds are debt securities issued by private and public companies.
- Investment class. …
- High yield. …
- Municipal bonds, called “munis,” are debt securities issued by states, cities, counties, and other government entities.
Are Treasury bills highly marketable?

The return on these types of securities is low, due to the fact that marketable securities are highly liquid and are considered safe investments. Examples of marketable securities include ordinary shares, commercial papers, bankers’ acceptances, treasury bills and other money market instruments.
Do US Treasury securities have a marketable risk? Although treasuries are considered to have very low free credit risk, they are affected by other types of risk, mainly interest rate risk and inflation risk. Similarly, if interest rates fall, the value of the older bond that is paid more will increase compared to new issues. …
Are Treasury bonds marketable?
Marketable securities consist of treasury bills, bills, bonds, inflation-protected securities (TIPS), floating rate (FRN) bonds and Federal Finance Bank (FFB) securities. … Non-marketable securities are not transferable or transferable and are not sold on the secondary market.
Are Treasury bonds marketable securities?
Most non-marketable securities are government debt instruments. … The most widespread market securities include U.S. Treasury bills and treasury bonds, which are freely traded on the U.S. bond market.
Are Treasury strips marketable?
US Treasury Securities Treasury securities fall into two categories – marketable and non-marketable. After the original issue by the Treasury, marketable securities can be bought and sold on the financial market, and ownership is transferable.
Are government bonds marketable?
U.S. savings bonds, rural electrification certificates, a series of government and local government securities, and a series of government account bonds are not marketable. These are also examples of debt securities. Non-marketable securities are often issued at a discount and are expected to reach their face value over time.
Are Treasury bills marketable?
Treasury bills or treasury bills have a maximum maturity of 364 days. Thus, they are categorized as money market instruments (the money market operates with assets with a maturity of less than one year).
Can you make money buying Treasury bills?
Treasury bills are one of the few investments you can make for just $ 100. … In general, the longer the maturity, the more money you will make from your investment. The face value of a treasury bill is called its face value, and the most commonly sold bills have a face value of between $ 1,000 and $ 10,000.
Are bonds marketable securities?
Shares, bonds, short-term commercial papers and certificates of deposit (CDs) are considered marketable securities because there is a public demand for them and can be easily converted into cash.
Are Treasury bills worth buying?
Treasury bills are one of the safest investments, but their returns are low compared to most other investments. Opportunity cost and risk need to be considered when deciding whether treasury bills are eligible for the retirement portfolio. In general, treasury bills may be appropriate for investors who are close to or retired.
Do treasury bills have high returns?
Treasury bills with longer maturities usually have higher yields than those with shorter maturities. In other words, short-term treasury bills are discounted less than long-term treasury bills.
Do treasury bills have higher returns than stocks?
Due to the higher risk associated with stocks, they traditionally provide much higher returns than treasury bills. For example, stocks returned an average of 11.2 percent annually from 1928 to 2011, while treasury bills returned only 3.66 percent, according to Stern Business School at New York University.
What is the return on Treasury bills?
As of February 7, 2020, the Treasury yield on quarterly treasury bills is 1.56%; A 10-year bond is 1.59% and a 30-year bond is 2.05%. The U.S. Treasury Department publishes yields on all of these securities on its website on a daily basis.
Are Treasury bonds high return?
Bad bonds Higher interest rates result in higher yields. Bonds issued by the U.S. government, including U.S. Treasury bills, bonds and bills, offer some of the lowest available interest rates, which is why treasury bonds are not in the class of bonds called ‘high-yield’ bonds.
Are T-bills safer than CDs?

Both treasury bills and CDs are extremely safe investments. The vaults are backed by the full faith and credit of the United States. … CDs are supported by the FDIC up to $ 250,000 per institution, per individual, for each account ownership category.
What is better treasury bills or CDs? Compared to other types of bonds, treasury bonds typically pay lower interest rates because default risk and credit risk are much lower. … Depending on the conditions, the CD may offer a fixed or variable interest rate. The interest rates offered by banks for CDs are affected by the interest rate set by the Federal Reserve.
Are T-bills a safe investment?
Treasury bills are considered safe and conservative investments as they are supported by the US government. Treasury bills are usually held until the maturity date. However, some owners may want to pay out the money before maturity and make short-term interest income by reselling the investment in the secondary market.
Can you lose money on T-bills?
Treasury bonds are considered risk-free assets, which means that there is no risk that the investor will lose the principal. In other words, investors who hold the bond to maturity are guaranteed their principal or initial investment.
Why are T-bills considered among the safest investments?
They are considered among the safest investments because they are backed by the full faith and credit of the United States Government. When an investor buys a treasury bill, he lends money to the state. The U.S. government uses the money to finance its debt and pay its running costs.
Can you lose money on T-bills?
Treasury bonds are considered risk-free assets, which means that there is no risk that the investor will lose the principal. In other words, investors who hold the bond to maturity are guaranteed their principal or initial investment.
What are Treasury bills?
Treasury bills are short-term government securities with a maturity of several days to 52 weeks. Bills of exchange are sold at a discount of their face value.
Are Treasury bills better than cash?
If you keep a treasury bill, bill of exchange or bond to maturity, you are guaranteed to return at least the value of the original investment. There is a risk that treasuries lose value due to inflation or if they are sold before maturity when interest rates are high.
Are T bills safer than cash?
The risk of the treasury failing to meet its payment obligation is essentially zero, as the federal government can always print money to pay the debt. Treasury bills therefore do not carry repayment risk and are safer than investment funds.
